몽고db에서 자주 사용되는 집계함수 기능에 대해서 정리하여 보았다.
1. body 컬렉션 내용은 아래와 같다.

2. head 컬렉션 내용이다.

3. 단순 집계 기능이다. 조회, 그룹핑, 카운트 및 합계이다. 대상은 body 컬렉션이다. as 메소드는 불리우는 이름이다.
public void simpleSingle(){
Aggregation agg = null;
AggregationResults<HashMap> results = null;
agg = Aggregation.newAggregation(
Aggregation.project() //1. 매핑할 이름
.and("text").as("text_conv") //2.기존 도큐먼트 이름 바꾸기 가능
.and("type").as("type")
.and("date").as("date")
.and("number").as("number"),
Aggregation.match( //3. 날짜비교
new Criteria().andOperator(
Criteria.where("date").gte(LocalDateTime.parse("2019-09-01T00:00:00")).lte(LocalDateTime.parse("2019-09-30T23:59:59"))
)
),
Aggregation.group("type").count().as("total").sum("number").as("number") //4.그룹핑할 대상, 각 대상의 총 합은 total로 한다. number는 합계
);
results = template.aggregate(agg, "body", HashMap.class);
if(results != null){
List<HashMap> target = results.getMappedResults();
target.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
4. first와 last를 포함한 메소드이다. 집계하는 컬렉션 대상을 그룹할 때 가장 처음값과 마지막 값을 묶어준다.
public void simpleFirstAndLast(){
Aggregation agg = null;
AggregationResults<HashMap> results = null;
agg = Aggregation.newAggregation(
Aggregation.project() //1. 매핑할 이름
.and("1").as("1") //2. 1을 준 이유는 집계하는 대상이 1개면 불필요한 매핑이 되는 버그가 있다. 결과에는 아무런 문제 없다.
.and("text").as("text_conv") //3. 기존 도큐먼트 이름 바꾸기 가능
.and("type").as("type")
.and("date").as("date")
.and("number").as("number"),
Aggregation.match( //4. 조건 null이 아닌것
new Criteria().andOperator(
Criteria.where("text_conv").ne(null)
)
),
Aggregation.group("type","1") //5. type으로 그룹핑 하되,
.first("text_conv").as("text_conv").last("number").as("number") //text는 처음 등록한 것만 가져오고, number는 나중에 등록한 것만 가져온다.
);
results = template.aggregate(agg, "body", HashMap.class);
if(results != null){
List<HashMap> target = results.getMappedResults();
target.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
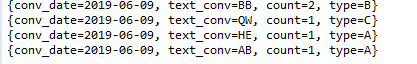
5. 문자열 및 날짜에 대한 처리 기능이다. substring을 활용해 문자열을 줄일 수 있고, dateAsFormattedString을 통해 날짜형태를 YYYYMMDD 등으로 원하는 방법데로 바꿀 수 있다.
public void simpleSubStringDateToString(){
Aggregation agg = null;
AggregationResults<HashMap> results = null;
agg = Aggregation.newAggregation(
Aggregation.project() //1. 매핑할 이름
.and("1").as("1")
.and("text").substring(0,2).as("text_conv") //2. 문자열 자르기 substring
.and("type").as("type")
.and("date").dateAsFormattedString("%Y-%d-%m").as("conv_date") //날짜파싱
.and("number").as("number"),
Aggregation.match( //3. 조건 null이 아닌것
new Criteria().andOperator(
Criteria.where("text_conv").regex("") //텍스트 전부 조건
)
),
Aggregation.group("type","conv_date", "text_conv").count().as("count")
);
results = template.aggregate(agg, "body", HashMap.class);
if(results != null){
List<HashMap> target = results.getMappedResults();
target.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
6. body 컬렉션과 head 컬렉션을 합쳐서(join) 결과를 나타낸다. 서로 가지고 있는 type이라는 도큐먼트 속성을 참조키로 사용한다. LookupOperation클래스를 여러개 활용해서 여러 항목을 묶을 수 있다. 여기서는 1개이다.
public void simpleLookUp(){
Aggregation agg = null;
AggregationResults<HashMap> results = null;
LookupOperation lookUp = LookupOperation.newLookup()
.from("head").localField("type") //1. 묶을 컬렉션 이름은 head, 대상 도큐먼트는 같은 이름인 type
.foreignField("type").as("ref"); //2. 조회할 컬렉션에서 해당 head 컬렉션이 묶일 도큐먼트 이름은 type, 별명은 ref
agg = Aggregation.newAggregation(
lookUp, //3. Join 개념
Aggregation.project() //4. 매핑
.and("type").as("type")
.and("ref").as("ref")
.and("text").as("text"),
Aggregation.match(
new Criteria().andOperator(
Criteria.where("text").regex("") //5. 텍스트 전부 조건
)
),
Aggregation.group("type", "ref")
);
results = template.aggregate(agg, "body", HashMap.class);
if(results != null){
List<HashMap> target = results.getMappedResults();
target.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
7. body 컬렉션과 head 컬렉션을 합치는데 원하는 특정 1개의 조건의 필드만 가져오게 한다. Projection부분이 핵심이다. arrayElementAt 메소드의 인자값은 배열의 순서이며 0,1,2,3...순서로 증가하고 -1은 끝 값을 의미한다.
public void simpleLookUp2(){
Aggregation agg = null;
AggregationResults<HashMap> results = null;
LookupOperation lookUp = LookupOperation.newLookup()
.from("head").localField("type") //1. 묶을 컬렉션 이름은 head, 대상 도큐먼트는 같은 이름인 type
.foreignField("type").as("ref"); //2. 조회할 컬렉션에서 해당 head 컬렉션이 묶일 도큐먼트 이름은 type, 별명은 ref
agg = Aggregation.newAggregation(
lookUp, //3. Join 개념
Aggregation.project() //4. 매핑
.and("type").as("type")
.and("ref").arrayElementAt(-1).as("ref1") //5. 참조 컬랙션 가장 마지막 가져오기
.and("ref").arrayElementAt(0).as("ref2") //6. 참조 컬랙션 가장 처음 가져오기
.and("text").as("text"),
Aggregation.match(
new Criteria().andOperator(
Criteria.where("text").regex("") //7. 텍스트 전부 조건
)
),
Aggregation.group("type", "ref1", "ref2")
);
results = template.aggregate(agg, "body", HashMap.class);
if(results != null){
List<HashMap> target = results.getMappedResults();
target.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
8. 행으로된 내용을 1개의 대상으로 배열형태로 묶어준다. 특정 도큐먼트를 풀어서 조건에 맞게 그룹화 된 데이터에 배열형태로 들어가게 된다. UnwindOperation 클래스가 해당 역할을 해 준다.
public void simpleUnwind(){
Aggregation agg = null;
AggregationResults<HashMap> results = null;
UnwindOperation unwind = Aggregation.unwind("text"); //1.행으로 이루어진 대상을 1개의 열로 배열 형태로 풀 도큐먼트
agg = Aggregation.newAggregation(
unwind,
Aggregation.project() //2. 매핑
.and("type").as("type")
.and("1").as("1")
.and("text").as("text"),
Aggregation.match(
new Criteria().andOperator(
Criteria.where("text").regex("") //3. 텍스트 전부 조건
)
),
Aggregation.group("type", "1").push("text").as("text") //4. push를 활용한 배열로 만든 text필드값 넣어주기
);
results = template.aggregate(agg, "body", HashMap.class);
if(results != null){
List<HashMap> target = results.getMappedResults();
target.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
* 이상 자주사용되는 집계함수의 내용이다.
'몽고DB > Java 몽고DB' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 몽고DB 트랜잭션을 위한 리플리카 셋, 적용 테스트(Mongodb transaction, Mongodb replica set) (5) | 2019.11.26 |
|---|---|
| Java Mongodb 연동, Java 몽고db 연동 (4.0이상 버전) (0) | 2019.11.26 |
| MongoTemplate Aggregate 사용간 파싱 버그 (0) | 2019.07.19 |
| MongoTemplate Aggregate (0) | 2019.06.21 |
| 스프링(전자정부), 몽고DB와의 연동 (몽고DB 터널링, Mongodb Ternering, Mongodb ssh) (14) | 2019.05.09 |




댓글